In addition to advancing pepinemab for both neurology and oncology indications, Vaccinex has programs in preclinical development.
VX5/5261 is a fully human monoclonal antibody selected through Vaccinex ActivMAb® technology that specifically binds human, primate and rodent CXCL13, a cytokine that triggers formation of organized lymphoid tissues at sites of inflammation and is linked to the development of autoimmunity.VX5/5261 neutralizes CXCL13 activity and has been shown to provide therapeutic benefit in mouse models of human autoimmune diseases (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis).
Pre-clinical development of VX5/5261 antibody has been initiated in preparation for filing an FDA Investigational New Drug (IND) application for the treatment of autoimmune disorders. Findings from some of our preclinical work are highlighted in Figures 1 and 2.
Figure 1
Click to enlarge
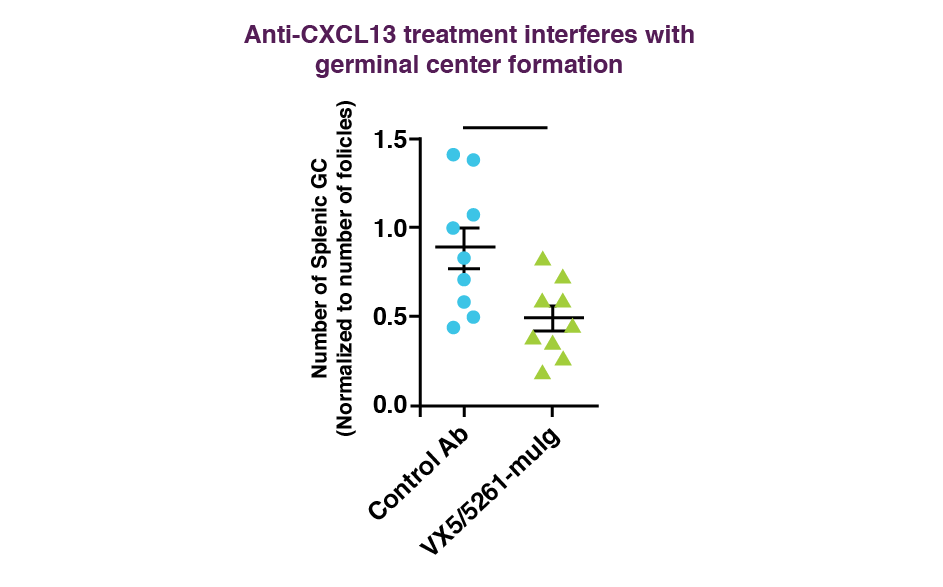
Effect of VX5/5261-muIg on germinal center formation in C57BL/6 mice challenged with NP-KLH.
Mice were treated with 30 mg/kg of VX5/5261-muIg antibody and corresponding mouse isotype control, on days -3, 0 (the day of the challenge), 4 and 7 (n=9/group). Number of PNA+ germinal centers in relation to total number of follicles per group was calculated using ImagePro software. *P = 0.01
Figure 2A and 2B
Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge
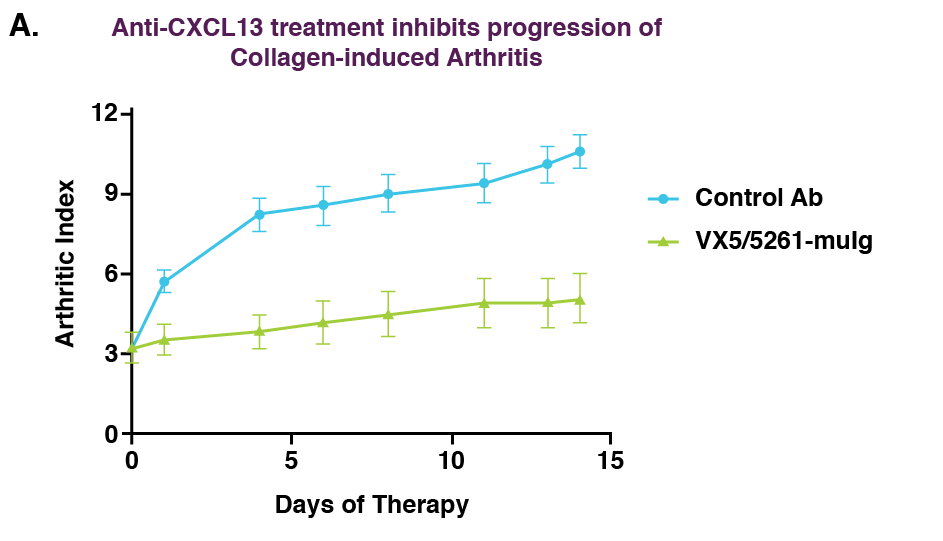
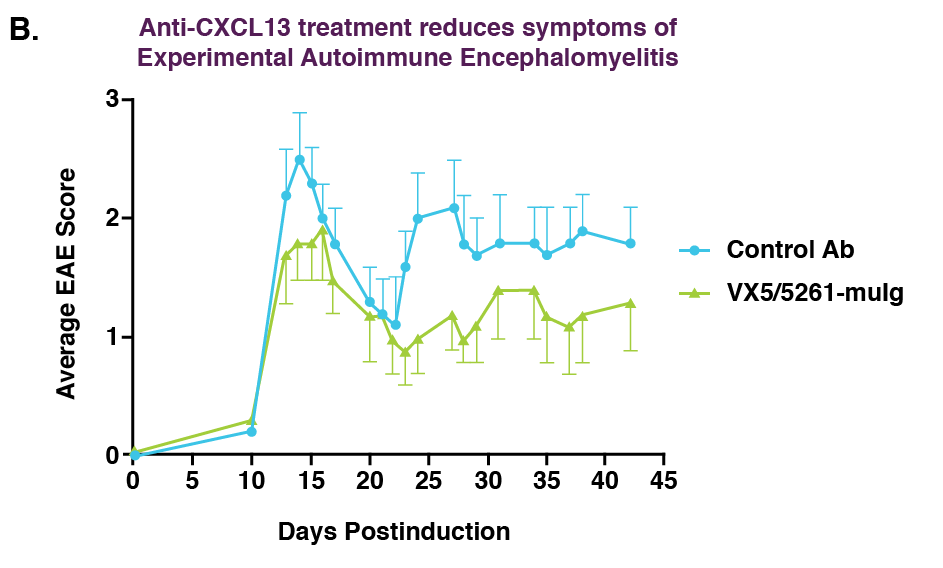
Effect of treatment with VX5/5261-muIg on CIA (A) and relapsing-remitting EAE (B).
(A) Male DBA1/J mice were subjected to therapeutic treatment regimen that was initiated when the group mean arthritic index (AI) reached 3-4 (approximately on day 30 post-initial immunization) and consisted of bi-weekly intraperitoneal injections of 30 mg/kg of the antibodies.
(B) Starting on day 7 post-immunization with PLP139-151, female SJL/J mice were treated with weekly intraperitoneal injections of 30mg/kg of the antibodies.
CXCL13, also known as B-cell attracting chemokine, is expressed by follicular dendritic cells (FDC) and macrophages. Through its receptor expressed on a variety of immune cells, it induces intracellular changes necessary for maintenance of immune system homeostasis, lymphoid organogenesis, leukocyte trafficking and chemotactic migration. In a chronically-inflamed environment, ectopic germinal centers form within affected (often non-lymphoid) tissues. CXCL13 over-expression in these germinal centers, accompanied by dysregulation in the interactions among other immune cells, is thought to interfere with elimination of autoreactive B cells and can result in aberrant inflammatory activity and may give rise to autoimmune diseases.
The CXCL13-mediated signaling pathway, therefore, represents an attractive target for the treatment of autoimmune disorders. Our VX5/5261 antibody efficiently neutralizes both mouse and human CXCL13 activity in several in vitro functional assays.
Click to enlarge
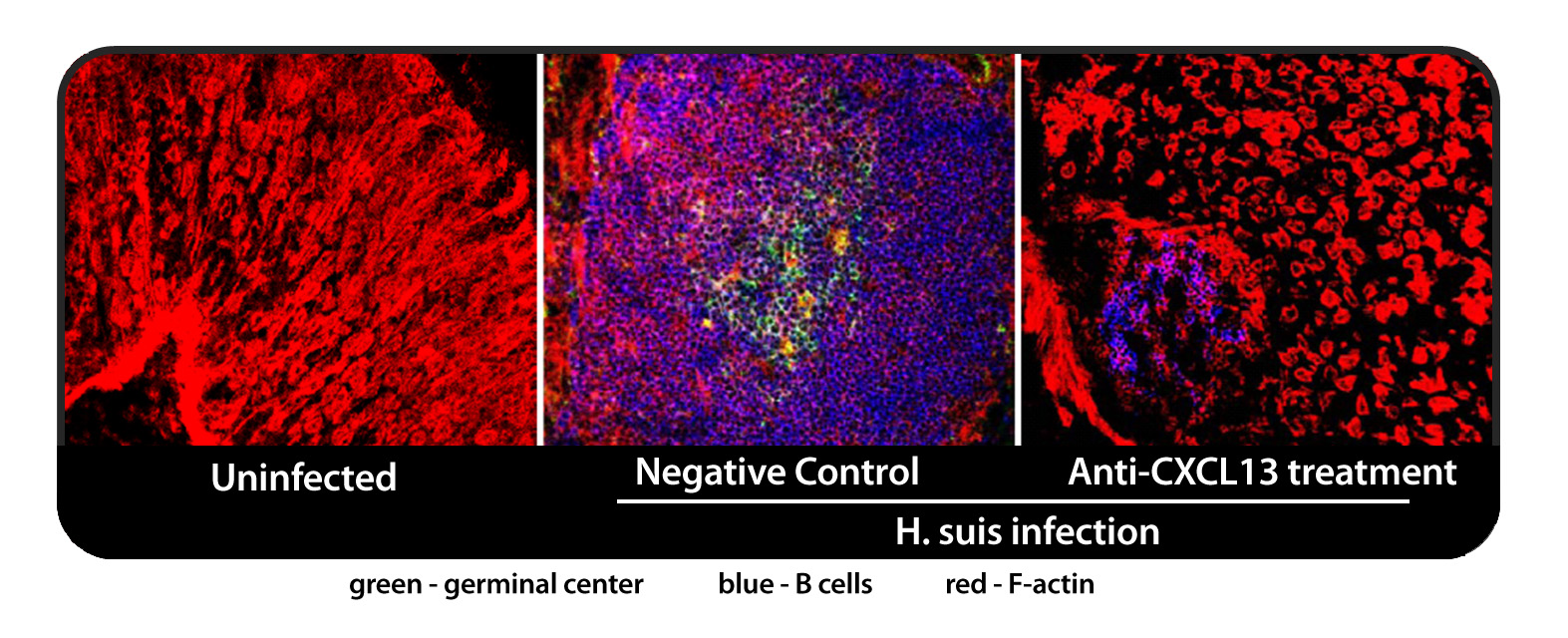
Anti-CXCL13 antibody suppresses Germinal Center Formation in Gastric Lymphoid Follicles
Induced by H. suis infection
In addition to autoimmunity, collaborative research between Vaccinex and scientists at Kobe University in Japan have linked overexpression of CXCL13 to inflammatory events that can lead to mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphomas. This suggests that blockade of CXCL13 may reduce the risk of cancer in certain chronic inflammatory conditions. Mucosal Immunol 7:1244-54, 2014.